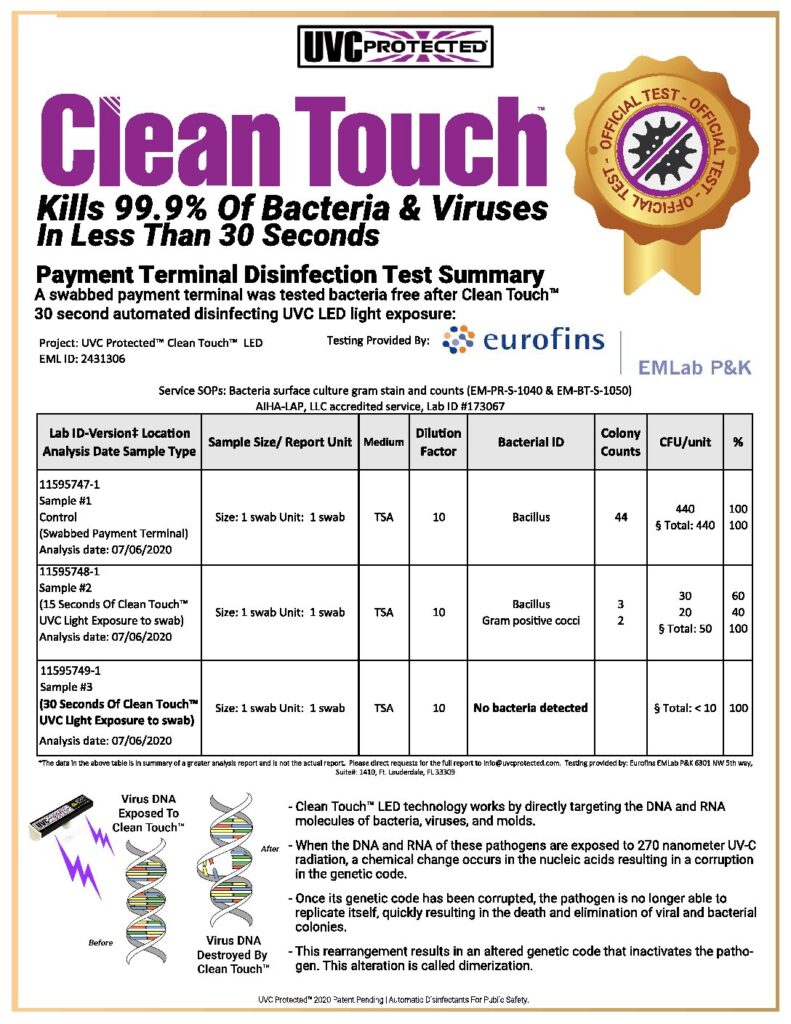
Destroys 99.9% Of Surface Bacteria & Viruses In 30 Seconds
The high energy from short wavelength UVC light is absorbed in the cellular RNA and DNA, damaging nucleic acids and preventing microorganisms from infecting and reproducing. This absorption of UVC energy forms new bonds between nucleotides, creating double bonds or “dimers.” Dimerization of molecules, particularly thymine, is the most common type of damage incurred by UVC light in microorganisms. Formation of thymine dimers in the DNA of bacteria and viruses prevents replication and ability to infect.